Feedback loop: what it is, steps and importance for Product
The Product routine is based on discovering opportunities with users, validating hypotheses, analyzing data, and applying improvements…
The Product routine is based on discovering opportunities with users, validating hypotheses, analyzing data, and applying improvements. That is, we are talking about a constant improvement cycle, which can also be called a feedback loop.
This process, as important as creating innovative solutions, is a pillar for those who want the best results in Product Discovery. Therefore, here in this article, we will explain what the concept is all about and what steps are part of successful execution.
What is a feedback loop?
A feedback loop is a concept spread by Eric Ries through his famous book “ The Lean Startup ”. In the publication, he brings the term to the context of disruptive companies, uniting the concepts of experimentation, validation, and agility to propose a model of continuous interaction.
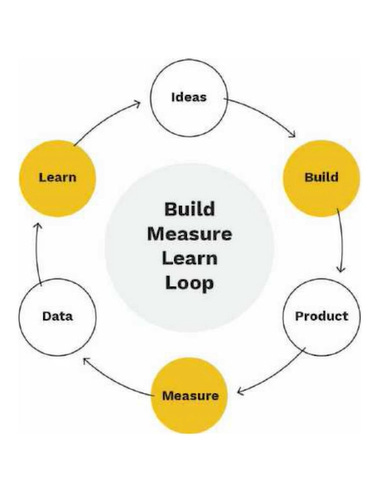
What are the steps of the feedback loop?
As the purpose of the feedback loop is to improve continually, the three main steps complement each other, forming a circle. They are: build, measure and learn.
Ramp up
Once you identify problems and opportunities, it’s time to start building what will be the solution, doing tests to generate as much learning for the flow ( MVP construction ). At this stage we are talking about the entire process, such as wireframes, mockups, prototypes, user testing, development, and QA.
Measure
This is the stage in which we analyze the results generated by our feature or product launch. Experiments (such as A/B testing and the Sean Ellis Survey ) will help you continually identify whether user needs are being met and whether you are on the right path.
You will generate a continuous learning cycle by capturing quantitative and qualitative data from transactions or product usage through Product Analytics tools.
For this, it is important to have clarity of your main KPIs , which will indicate if you are on the right path. Some examples that might be important: NPS , Churn, Retention, and ARPU.
Learn
It is time to look at the result of each test and gather lessons that can modify the hypotheses raised previously, generating new insights for the next cycle.
In this context, closing dynamics in project management are very useful, such as creating post-mortem documentation. To understand better, check out an example of how this step can be conducted.
Inputs needed to run the feedback loop
Ideas
Ideas come from creativity and also from the study of opportunities.
Therefore, Product Designers and UX Designers, for example, mainly contribute with the creative part. Meanwhile, Business Analysts , Market Intelligence Analysts and Product Marketing Managers , on the other hand, are some professionals who can help with a more niche view on the target market.
Product
The building part of the product itself will require efforts from Product Managers, Product Marketing Managers, and Development.
Building the MVP and structuring the entire product roadmap are some of the responsibilities that will allow you to move on to the measurement stage. Growth Product Managers will also get involved applying the Pirate Funnel , selecting the best tests and metrics to validate the product version.
Data
For the feedback loop to be consolidated — and, consequently, for measurement to become learning — Data Product Managers , Growth Product Managers, and Product Analytics specialists, in general, are key pieces.
These professionals are able to apply data visualization best practices, organizing and presenting data in ways that make sense across the enterprise.
In this way, it is possible to align stakeholders regarding results better and deliver the necessary insights to the team for a new development cycle.
How important is the feedback loop for the Product?
The feedback loop is a strategic management process for companies working with digital products. With the rapid changes that the market is experiencing in the current context, tests and validations ensure that the company is following the product life cycle, making safer decisions about the next step.
Here it is worth mentioning some important paths that a product can follow based on the results obtained with the feedback loop : iterate, pivot or persevere.
Iterate:small change to the product, in an attempt to generate more learning or improve the result generated;
Pivot:change in the direction of the business model, strategy or problem identified, in an attempt to correct the direction to the right path;
Persevere: experiments and evidence that validate your hypotheses, signaling that you should move on with the current model.